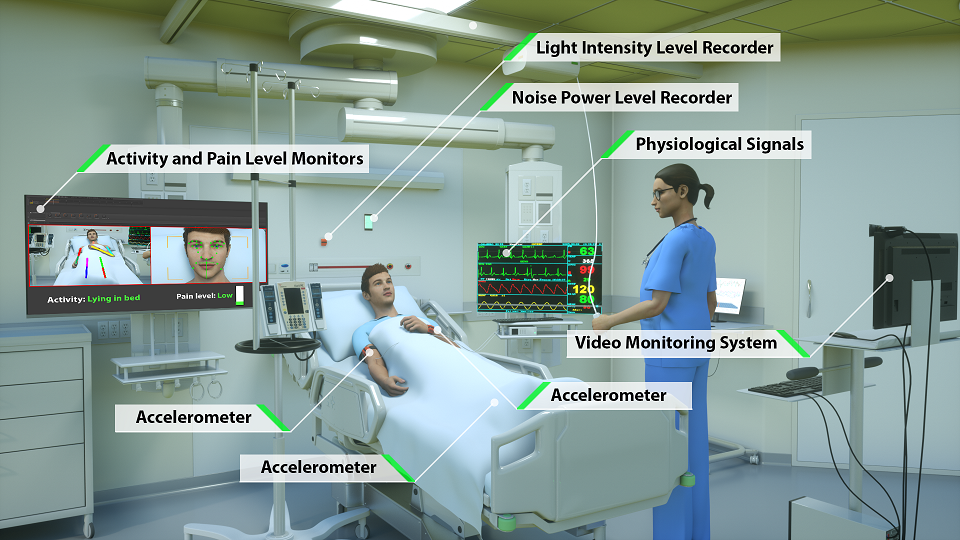
Currently, many critical care indices are repetitively assessed and recorded by overburdened nurses, e.g. physical function or facial pain expressions of nonverbal patients. In addition, many essential information on patients and their environment are not captured at all, or are captured in a non-granular manner, e.g. sleep disturbance factors such as bright light, loud background noise, or excessive visitations. In this pilot study, we examined the feasibility of using pervasive sensing technology and artificial intelligence for autonomous and granular monitoring of critically ill patients and their environment in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). As an exemplar prevalent condition, we also characterized delirious and non-delirious patients and their environment. We used wearable sensors, light and sound sensors, and a high-resolution camera to collected data on patients and their environment. We analyzed collected data using deep learning and statistical analysis. Our system performed face detection, face recognition, facial action unit detection, head pose detection, facial expression recognition, posture recognition, actigraphy analysis, sound pressure and light level detection, and visitation frequency detection. We were able to detect patient’s face (Mean average precision (mAP)=0.94), recognize patient’s face (mAP=0.80), and their postures (F1=0.94). We also found that all facial expressions, 11 activity features, visitation frequency during the day, visitation frequency during the night, light levels, and sound pressure levels during the night were significantly different between delirious and non-delirious patients (p-value<0.05). In summary, we showed that granular and autonomous monitoring of critically ill patients and their environment is feasible and can be used for characterizing critical care conditions and related environment factors.